Can you swim? How many words can you read in a minute? Well, if you ask me, I cannot swim. But, I can read 230 words under a minute.
Ability is something that you can do. It might be something in the present or in the past.
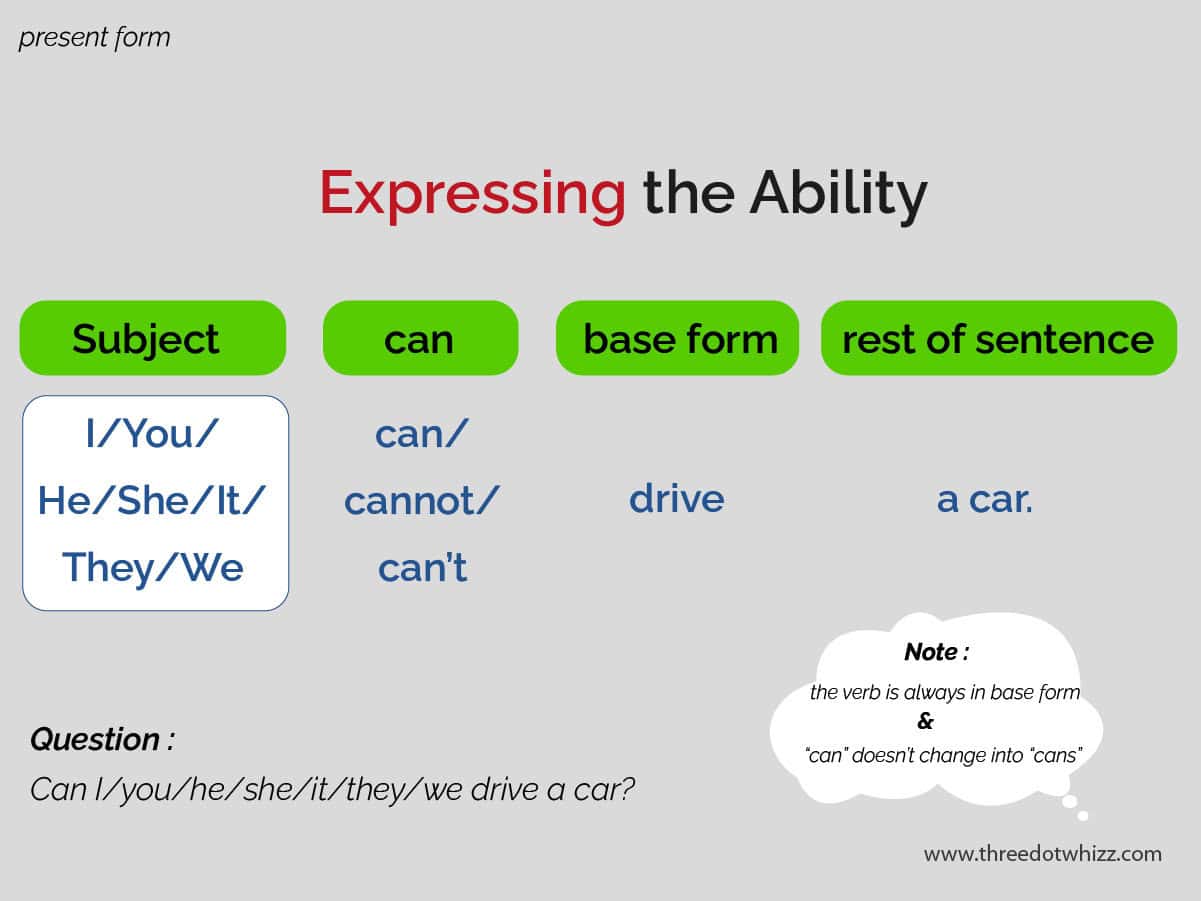
To express the ability, we use modal verbs can for the present and could for the past.
For example :
- I can drive a car.
- I cannot ride a bicycle.
- Can you ride a motorcycle?
- I could climb a mountain when I was a student.
But sometimes, there are moments where we prefer to express the ability with be able to.
Be able to is a verb phrase (not a modal verb), but we can use it to talk about the ability both in the present and the past.
Now, let’s look further into how to express ability using modal verbs can, could, and be able to.
1. Express ability in less formal context
In less formal context, we use modal verbs of ability can and could.
For example :
- I can drive a car.
- She can play guitar.
- They can sing folklore.
- I could climb mountains when I was younger. Now it’s hard for me.
- She could play guitar some years ago.
On those examples, the meaning of can is “know how to.” It usually refers to learned skills, such as driving a car, playing guitar, singing folklore, etc.
Now, compare these sentences :
I can cook = I know how to cook.
She can drive a truck = She know how to drive a truck.
For the abilities that most people have, we use can, because those abilities are always in the present.
Take a look at these examples :
- Humans can hold their breath for 30 to 90 seconds underwater.
- Cats can’t see well in the dark.
2. Talk about ability in formal context
In formal context, we prefer to use be able to in the present and past.
For example :
- The convention center is able to accommodate two thousand people.
- She was able to play guitar quite well.
3. Express what we sense and think
To express what we sense, we use this particular verbs : feel, hear, see, smell.
And for what we think : believe, remember, understand, imagine.
For example :
- I can’t imagine life without music.
I can feel something isn’t right here.
She can’t smell anything after that accident. - I couldn’t understand what she said.
She couldn’t see me from there.
4. Express passive voice
We use modal verbs of ability can and could before passives. We avoid using be able to here.
Examples :
The information can be found on the official website.
The details of the test can be read on page 130.
The project could be done faster if you use an AI.
If you are wondering what passives are, go to my post The Passive Voice (Your First Ultimate Guide) to get the ideas.
5. Inform possible future arrangement
For something that is arranged to be happen in the future, we can use can and be able to.
- The Prime Minister cannot attend the opening of the Olympic Games this year.
- The Prime Minister is not able to attend the opening of the Olympic Games this year.
- The city mayor can deliver a speech on this upcoming festival.
6. Talk about a situation which makes someone able or unable to do something
Sometimes there is a situation or term that makes you able or unable to do something. This may refer to the past, present, or future. Use can and be able to in these cases.
For example :
- The doctor can’t see you right now — she’s with another patient.
- I can help you with your project next week since I have some free time.
- We were able to finish the last project on time because we got extra help.
Wecouldfinish the last project on time because we got extra help. (wrong)
7. Talk about a specific achievement in the past
When we talk about a specific achievement in the past, we usually use be able to instead of could.
For example :
They were able to watch the soccer game because they arrived home earlier.
They could watch the soccer game because they arrived home earlier. (wrong)
Compare to these sentences :
(a) She could play guitar some years ago.
(b) She were able to play guitar some years ago.
In (a) and (b), we express a general ability. That’s why could is possible to use.
However, when it is a negative achievement, we can use both could not and be not able to.
For example :
- The police were not able to locate the mafia.
- The security couldn’t prevent the riot from happening.
- I tried to get up, but I couldn’t move.
Talking about ability in other sentence structures
Most of the time, we use the modal verbs of ability can/could in the present and past tense. Sometimes you may encounter other forms of sentence, and you only can use be able to.
- I haven’t been able to reach him all day. (present perfect)
- My mother hates not being able to visit us every month. (-ing form)
- We have got to be able to host the economic forum this year. (infinitive)
- You should be able to complete that project this year. (after a modal)
- She will be able to join us tonight. (future simple)
They won’t be able to attend this annual event.
won’t be able = will not be able.
You may find will be unable instead of “will not be able,” but it is less common.
For example :
- She will not be able to join us tonight.
- She will be unable to join us tonight.
How to form can and be able to in the present and past
Now, let’s look on how to form the sentences to express the ability with modal verbs can/could and be able to in present and past.
Can in the present
“Can” has three negative forms : can’t, cannot, and can not.
The pronunciation of can and can’t might sound similar to you.
This is how you’re gonna differentiate them :
When you speak, don’t stress the word can and pronounce it as /kən/.
And, stress the word can’t and pronounce it as /kænt/.
If you’re learning British English, pronounce can’t as /kɑːnt.
You may want to check this Cambridge Dictionary to practice the pronunciation.
Can not is unusual in written English. You may not see it a lot. On top of that, some people consider it an incorrect spelling of “cannot”.
Therefore, it’s better to use cannot instead.
Here is how to form the expression.

Can in the past
The past form of “can” is could. And the negative form is could not or couldn’t.
Couldn’t is the contraction of could not and you may hear it more in spoken English.
Here is how to form the expression.

Be able to in the present
The negative form of “be able to” is be not able to. Or, you may say : unable to.
For example :
Sorry, I’m not able to help you.
Sorry, I’m unable to help you.
Here is how to form the expression.

Be able to in the past
In the past form, you just need to change the be into past. And just add not for the negative form.
Here is how to form it.

Well, that’s a lot of things to absorb. So, what’s the conclusion?
Conclusion
At this moment, you might feel a bit confused.
But, hold on tight; that’s normal when you are stuffed with a lot of information at one time.
To make it easier for you, I’ve summarized the use of be able to, can, and could to express the ability.
| Can | Could | Be able to | |
|---|---|---|---|
| mode | spoken | spoken | written |
| present time | yes | no | yes |
| past time | no | yes | yes |
| other structures | no | no | yes |
| style | less formal | less formal | formal |
| with verbs of thinking and sense | yes | yes | no |
| passive voice | yes | yes | no |
| future arrangement | yes | no | yes |
| future ability | no | no | yes |
| specific achievement | no | negative | positive and negative |
What you can do after reading this
Well, what’s the point of learning tedious grammar without even using it?
First, think back to why you landed on this page. Ask yourself: What am I looking for?
For instance, let’s say you wanted to double-check your homework about using “can” and “could.” You were looking for examples, so just hover over the section of this page where “can/could” is mentioned.
Then, forget about “be able to” for a while. We don’t use it as much as “can” and “could”. Then, come back again to learn more.
After that, make sentences with “can” and “could” in your journal. List some of your abilities and skills.
Try to remember things you’ve achieved, maybe some months or years ago.
And to make it a little bit fun, text some friends in English with some pop-up questions or challenges like:
- Could you dance when you were 5 years old?
- Can you read with one eye closed?
- Can you clap your hands behind your back?
- Are you able to wiggle your ears?
If you want to learn more about modal verbs, here are some useful posts that I’ve made for you :
Modal Verbs : How to Give Order and Advice
Modal Verbs: How to Ask for Permission and Make Requests
Grammar book reference
Azar, Betty, and Stacy Hagen. Understanding and Using English Grammar. Pearson Education, Hoboken, NJ, 2017.
DK. English for Everyone: English Grammar Guide: A Comprehensive Visual Reference. DK Publishing (Dorling Kindersley), 2016.
Hewings, Martin, and Simon Haines. Grammar and Vocabulary for Advanced: With Answers. Cambridge University Press, 2016.
Thomas, Barbara, et al. Grammar and Vocabulary for First and First for Schools Book with Answers and Audio. Cambridge University Press, 2015.
What can I do for you?
Although I claim to cover everything about expressing ability using these modals, I do always leave room for improvement.
You may encounter another expression that I haven’t heard or seen before.
Do you mind sharing your thoughts about it? It would be a huge help for me!
Even better, connect with me here and throw me your questions. I occasionally update this article, so subscribe here to receive more updates.
If you have any doubts, just let me know!